Abstract
Introduction
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is the most common long-term complication and also a major cause of death after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT), frequently involving skin, digestive tract, liver, and lung. Corticosteroids are the first-line treatment and immunosuppressants are usually the second-line treatment for GvHD, but they have limited efficacy for steroid-refractory-GvHD (SR-GvHD). Ruxolitinib an oral tyrosine kinase-Janus kinase (JAK) 1/2 inhibitor was approved by FDA for the treatment of SR-GvHD. As direct head-to-head trials of Ruxolitinib in Chinese patients are not available, it was necessary to carry out systematic review and meta-analysis (SR&MA) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Ruxolitinib in Chinese patients with SR-GvHD.
Methods
The present study was performed in accordance with the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis) statement. We searched the MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library and relevant databases for clinical and observational studies evaluating the efficacy and safety of Ruxolitinib in Chinese patients with confirmed SR-GvHD from inception to December 2021. Data from the included studies was extracted in predefined extraction grid and study quality was evaluated to identify risk of bias. Outcomes of interest included overall objective response rate (ORR), complete response (CR), partial response (PR), non-response (NR); proportion of hormone reduction and withdrawal; overall survival (OS), mortality, safety, and tolerability. Meta-analysis of the included studies was performed using the Cochrane Collaboration recommended systematic review method and software (Stata 16).
Results
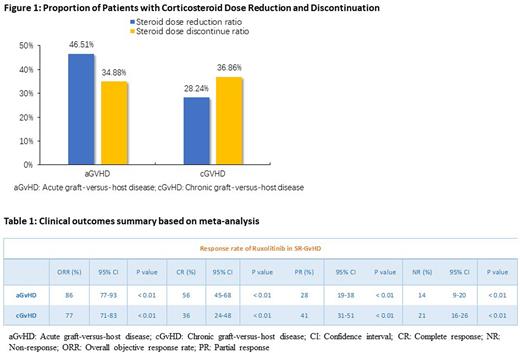
A total of 19 case series and cohorts with 775 patients with age between 0.9 to 64 years were included in the study. Ruxolitinib was administered at a dose of 10 to 20 mg/day, of which 561 (72.4%) received 5 to 10 mg bid. Among 339 patients with acute GvHD and 431 patients with chronic GvHD included in 13 studies, ORR, CR, PR, and NR were 86% and 77%, 56% and 36%, 28% and 41% and 14% and 21%, respectively (Table 1). The ORR in the subgroup of patients with skin, gastrointestinal and liver-GvHD was the highest among patients with aGvHD and cGvHD (85% and 84%, 73% and 71%, 69% and 70%) respectively. Four studies described a dose reduction or discontinuation of Corticosteroids: aGvHD (46.51% and 34.88%) and cGvHD (28.24% and 36.86%), respectively (Figure 1).
Twelve months OS was reported in four studies, including 404 patients, 179 with aGvHD and 225 with cGvHD. Overall, 12-month survival was 71% (95% CI 63% -79%); aGvHD: 66% (95% CI 56% -76%) and cGvHD: 76% (95% CI 56% -76%), respectively. Among 579 patients with SR-GvHD; 298 with aGvHD and 281 with cGvHD, resulting in an overall mortality rate of 26% (95% CI 19% -34%); aGvHD: 31% (95% CI 21% -42%) and cGvHD: 21% (95% CI 12% -32%) respectively. Eighteen studies reported 760 adverse reactions, and 287 viral infections (36.0%) and 269 cytopenias (34.7%) were the most common adverse reactions. Briefly, Cytomegalovirus infection (18.7%) and Epstein-Barr virus infection (10.8%), thrombocytopenia (12.9%) and hemoglobin (11.1%) were the most frequent Cytopenias.
Conclusion
Results of the meta-analysis showed that Ruxolitinib could have a positive effect in the treatment of SR-GvHD in the Chinese population. Ruxolitinib was able to significantly reduce or discontinue steroid dosage in patients with SR-GvHD. The adverse drug reactions were mainly cytopenias and viral infections consistent with observations of the REACH studies. Ruxolitinib was generally well tolerated, and no new safety signals were observed.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal